Understanding how to read your electric and natural gas bills every month is a vital part of keeping your business’ energy budget in check. When looking at your electricity bill or natural gas bill you might wonder what a kWh is, what a therm is, what electricity or natural gas supply charges are, how they are calculated or maybe you have other questions. Here at Consumer Energy Solutions we want to help you manage your energy expenses by providing the information you need about energy costs and how energy usage affects your monthly bills.
Understanding Your Electric Bill: Charges, Fees & How They’re Calculated
In order to understand your electric bill you need to learn what all the different line items are that appear on your business’ bill. Before we go any further, grab a copy of your electricity bill, or find a sample bill from your supplier/utility (your utility bill might include your supplier charges). Typically each bill is broken up into multiple charges that may vary slightly.
What are the charges and fees on my electric bill?
- Electricity Cost: If you look at your bill (or sample bill), you will see a page titled or section titled “Detailed Charges/Total Charges” or something similar. Once you are there, find the “Electric Supply Charge”, “Energy Charge”, or something similar. This is what you were charged for the electricity your business used in that billing period (typically 1 month) and it looks like this:
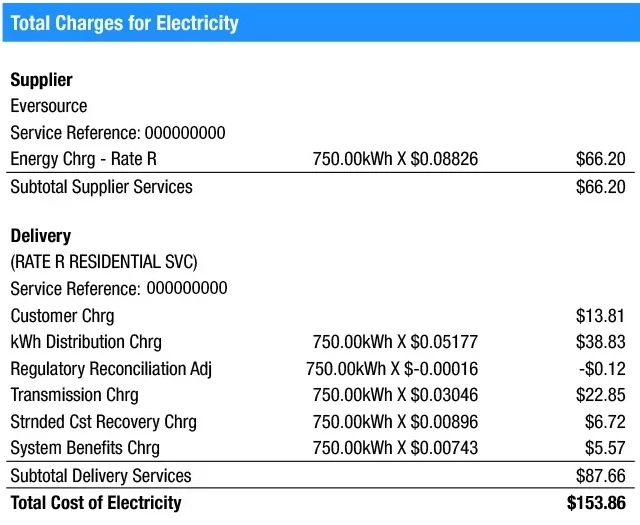
Your business’ total usage (kWh) multiplied by your rate determines how much your business is being charged. The 2 main ways you can have control over this portion of your bill are:
-
- You can reduce your business’ total usage.
- You can get a fixed rate from a retail energy supplier to avoid fluctuations in rates that occur due to weather, fuel prices, or other factors.
2. Electricity Capacity Charges: A capacity charge (sometimes referred to as demand charge) is what your utility charges your business to maintain the reliability of the electrical grid on days with the highest demand. For example, in the summer when you are cooling down your office building, most businesses/homes on the same transmission grid will be doing the same. On the hottest days of the year, electrical demand is normally the highest. Your utility company measures your usage on these days and gives your business a capacity tag based on that usage. The higher the usage, the more you pay in capacity charges. These charges often account for anywhere from 15% to 30% of a company’s electricity costs.
Looking to get lower energy rates?
Here are some things you can explore to reduce demand charges for your business:
-
- Utilizing your local utility’s Demand Response Program. These programs offer financial incentives for using less energy during the hours of peak demand. These programs vary from utility to utility so you will need to find out what program your utility offers for businesses.
- Taking advantage of energy efficient equipment is a great way to reduce your overall usage and demand charges. Many businesses cannot change their hours of operation or time usage of machines for off-peak hours so, using things like LED lighting, and Energy Star Certified equipment is the best solution.
3. Utility Delivery Charge: Another very common question is “what is the electricity delivery charge?” The delivery fee is what the utility charges you for maintenance and upkeep of the electrical grid, which helps ensure your home or business has constant power. The name of this charge might be “transmission fee” or something similar depending on the utility, but the impact on your bill remains.
What do kW and kWh mean on your Electric bill?
In order to fully understand how your bill is calculated you need to know the difference between kW and kWh.These terms are often interchanged, but they are actually 2 different forms of measurement. A kW is a kilowatt, a unit of measuring electricity equal to 1,000 watts. A kWh is a kilowatt-hour and is a unit of measure used to find out how much kilowatts a machine uses per hour.
How is the electricity portion of your bill calculated?
This is very simple, it is the total kWh used multiplied by your electricity rate. It will look like this:

Your business’ natural gas bill explained
Like electric rates, natural gas comes in fixed or variable rates which affects your monthly bill. Understanding your natural gas bill is a little more complex when you have a variable rate that changes month to month. Fixed-rate billing is less complex than variable rates as it keeps the rate you pay the same each month.
Natural gas bills are similar to electric bills, however there are a few terms that need to be defined to fully understand them:
What is a CCF? A CCF is a measurement of natural gas usage. This measurement represents a unit volume equal to 100 cubic feet.
What is a BTU? A British thermal unit, or BTU, is the measurement of how much energy is needed to raise the temperature of a pound of water by 1 degree Fahrenheit.
What is a Therm? A therm is the unit measurement of your natural gas usage over time. One Therm is equal to 100,000 BTUs.
What is Price Per Therm? This is the rate you pay per every Therm used, per your contract. This rate will vary due to the time of year, supply available, and other factors if you are on a variable rate plan.
Similar to electric bills you may have transmission fees, capacity fees, customer service fees and other charges based on your state and utility requirements.
Looking to get lower energy rates?